FACTS & FIGURES
What is Climate Justice?
Climate change arises primarily from human activities, notably the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas. This releases copious greenhouse gases (GHGs), such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, into the atmosphere. GHGs trap solar heat, leading to long-term shifts in weather patterns and rising global temperatures. These changes bring various environmental impacts:
1. Temperature Rise: Escalating GHG levels cause heatwaves and disrupt ecosystems.
2. Ice Melt: Higher temperatures result in ice caps and glaciers melting, endangering coastal regions.
3. Extreme Weather: Climate change intensifies hurricanes, droughts, floods, and storms, causing extensive destruction.
4. Altered Precipitation: Shifting weather patterns lead to more intense rainfall in some areas and droughts in others, impacting agriculture and water supply.
5. Ocean Acidification: Elevated carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are absorbed by oceans, making them more acidic and detrimental to marine life, particularly coral reefs and shellfish.
6. Biodiversity Loss: Ecosystem disruptions threaten species unable to adapt.
Climate justice centers on the ethical, political, and social dimensions of climate change. It acknowledges that marginalized communities, despite contributing minimally to GHG emissions, endure the severest consequences. Climate justice strives for human rights, social equity, equitable climate policies, a just transition to a low-carbon economy, and recognition of historical responsibilities. It champions a fair and sustainable future for all, particularly the most vulnerable, encapsulated in this 150-word summary.
How Does Climate Change affect Girls’ Human Rights?
-

RIGHT TO LIFE
Climate change can lead to extreme weather events and natural disasters, which can threaten girls' right to life and survival.
-

RIGHT TO HEALTH
Climate change can lead to poor air quality, heatwaves, and the spread of diseases. This affects their right to the highest attainable standard of health.
-

RIGHT TO FOOD
Climate change can negatively impact agriculture and food production, leading to food shortages and malnutrition. This affects girls' rights to adequate food and nutrition.
-
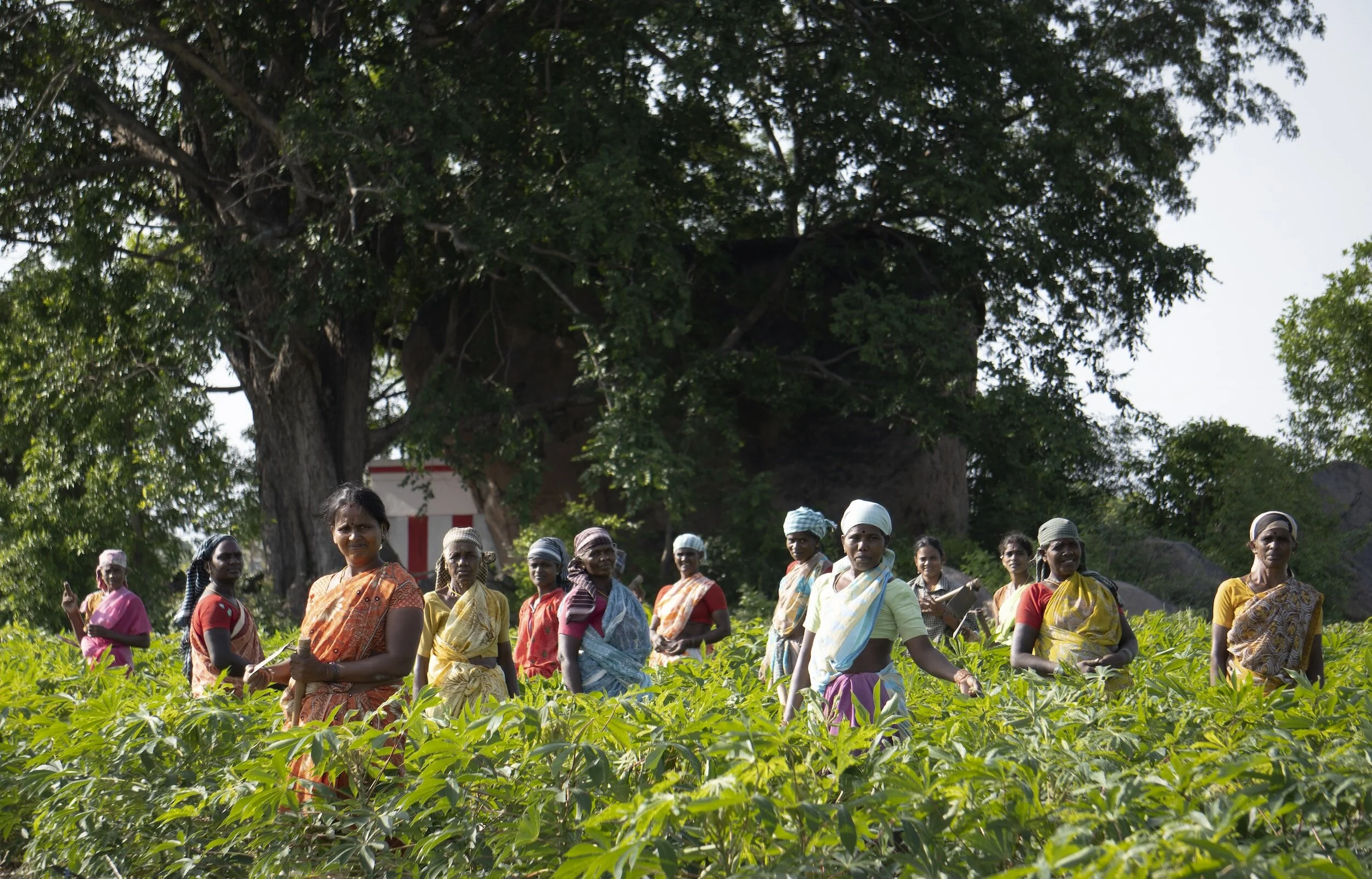

RIGHT TO WORK
Climate change can reduce economic opportunities in affected communities. This can limit girls' chances for financial independence and affect their right to work.
-
RIGHT TO EDUCATION
Natural disasters and extreme weather events, which are more frequent due to climate change, can damage or destroy schools, disrupt education, or force girls to miss school to help their families recover. This impacts their right to education.
-
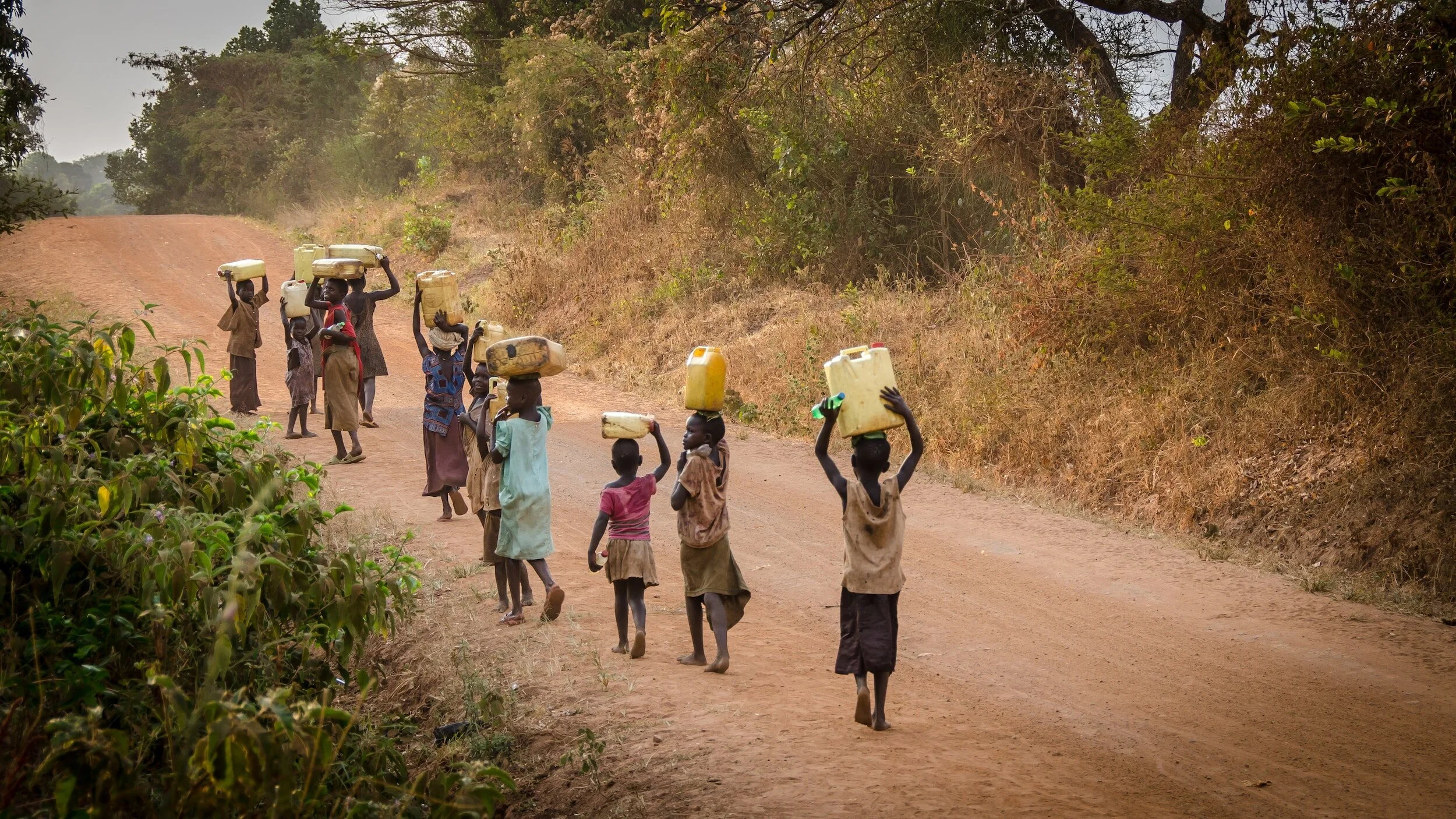

RIGHT TO WATER & SANITATION
Climate change can cause water scarcity, making it harder for girls to access clean water and sanitation. In many communities, girls are responsible for collecting water, which could mean longer walks and missed school time. This affects their rights to water, sanitation, and education.
-
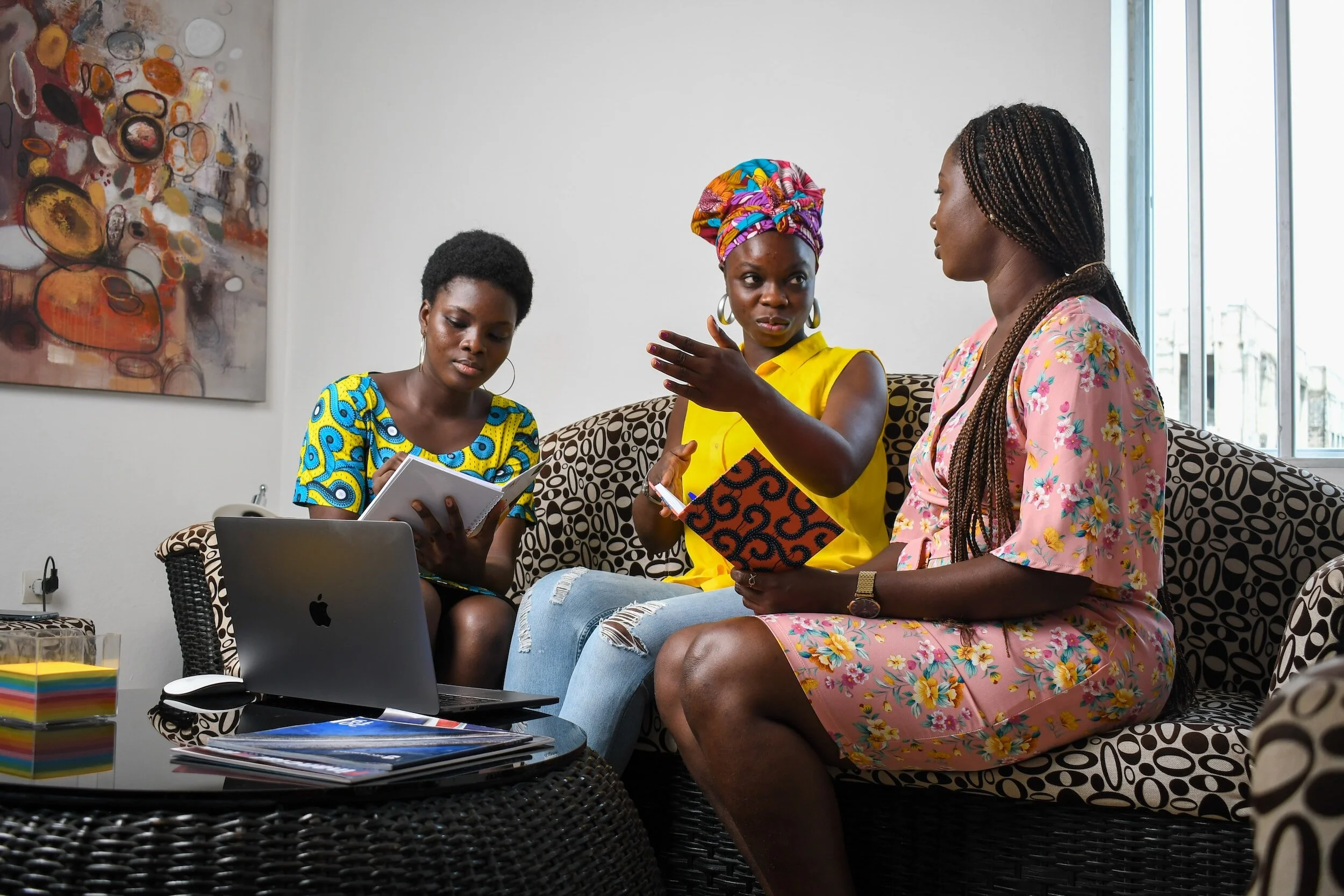

RIGHT TO PARTICIPATION
Girls should have the opportunity to participate in decision-making processes related to climate change and its impacts. However, their voices are underrepresented, affecting their right to participate in public life.
-
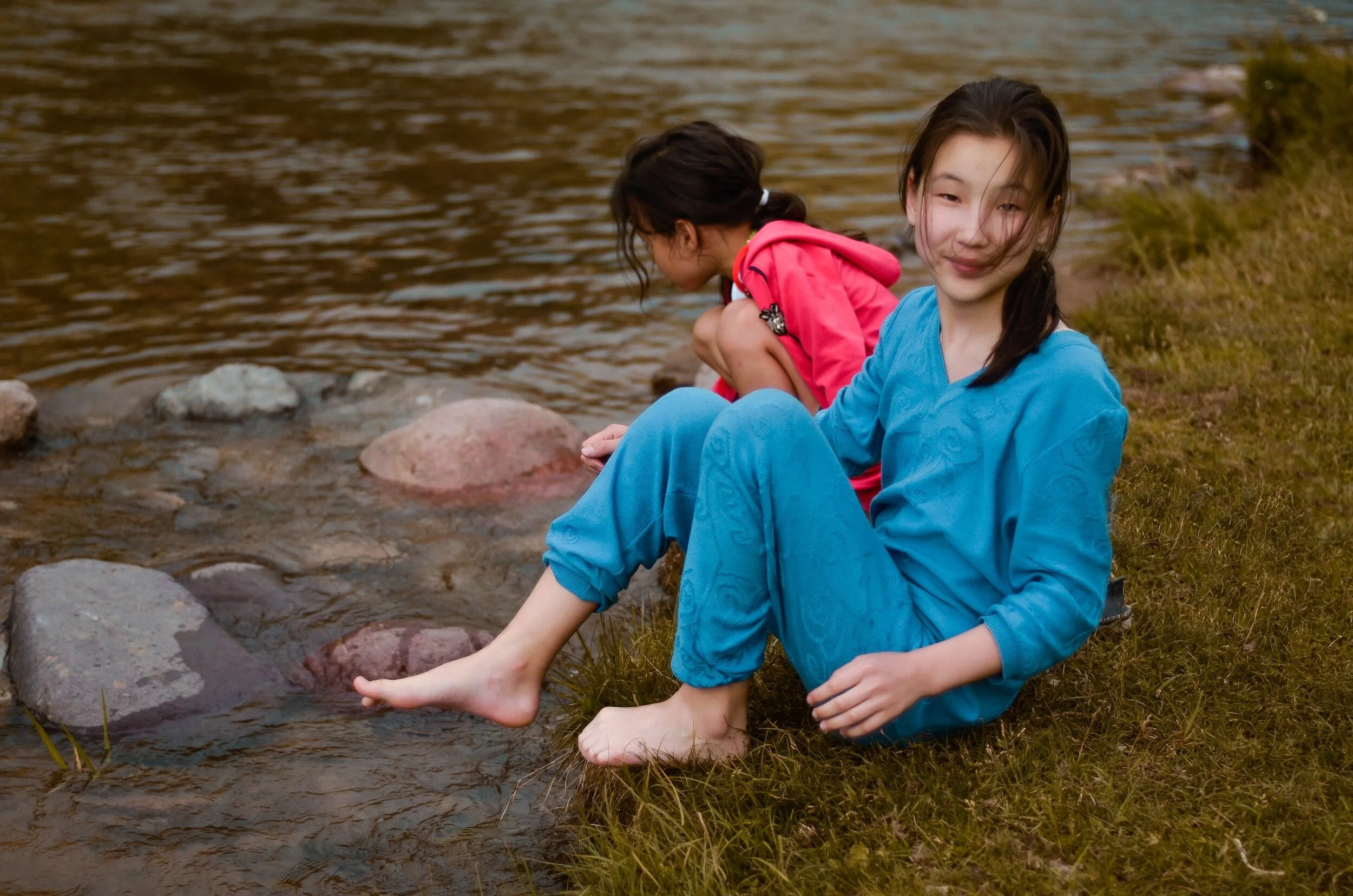

RIGHT TO SAFETY
Climate change can contribute to conflicts over resources, displacement, and migration. Girls in these situations may be more vulnerable to violence, exploitation, and trafficking, affecting their rights to safety and security.
The International Legal Framework
What Role Can Girls Play in Advocating for Climate Justice?
-
Learn about climate change, its impacts, and climate justice. Share this with friends, family, and the community to raise awareness and inspire action.
-
Participate in local, national, or international organisations dedicated to climate justice & activism, such as youth-led movements like Fridays for Future. Girls can also start their own clubs or initiatives at school or in their communities.
-
Write letters, sign petitions, or meet with local government representatives to demand stronger climate policies that prioritise justice & equity for marginalised communities.
-
Use social media platforms to share information, raise awareness, and mobilize others to join the fight for climate justice. Girls can also participate in online campaigns, webinars, and virtual events focused on climate issues.
-
Adopt eco-friendly habits, such as reducing waste, conserving energy, and supporting sustainable products & businesses. Encourage friends & family to do the same.
-
Volunteer or fundraise for organisations that promote climate justice, work on community resilience projects, or assist vulnerable populations impacted.
-
Join peaceful demonstrations and protests to demand urgent climate action and draw attention to the need for climate justice.




